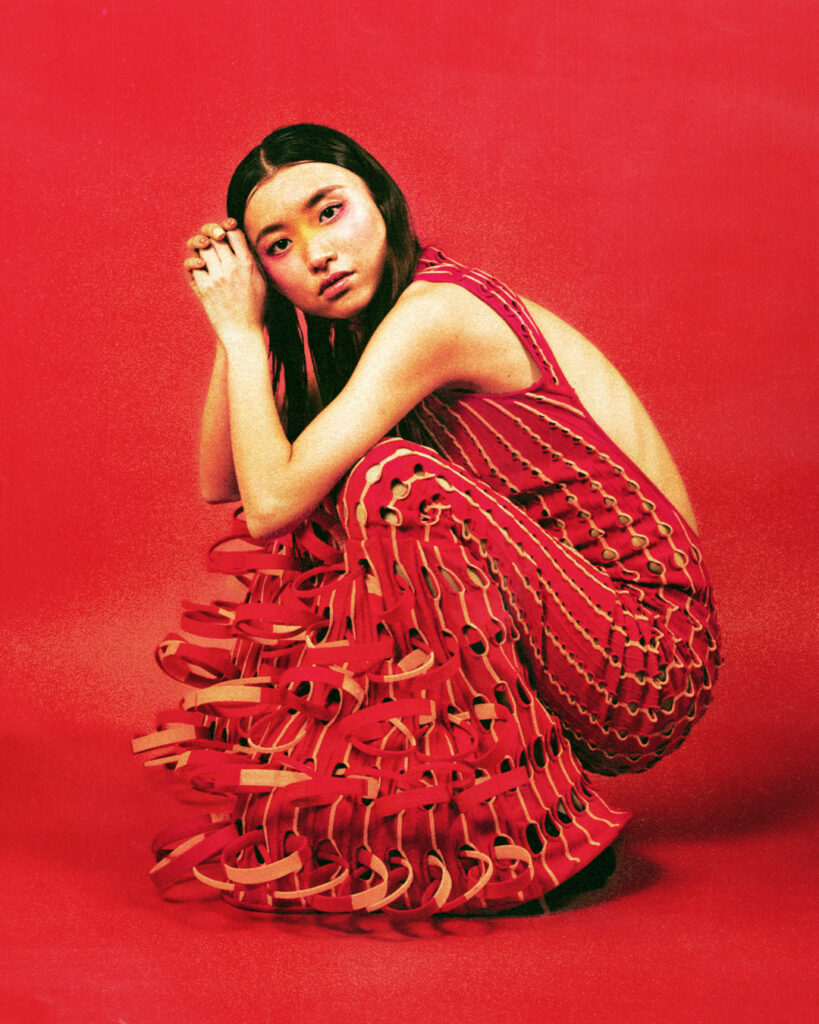
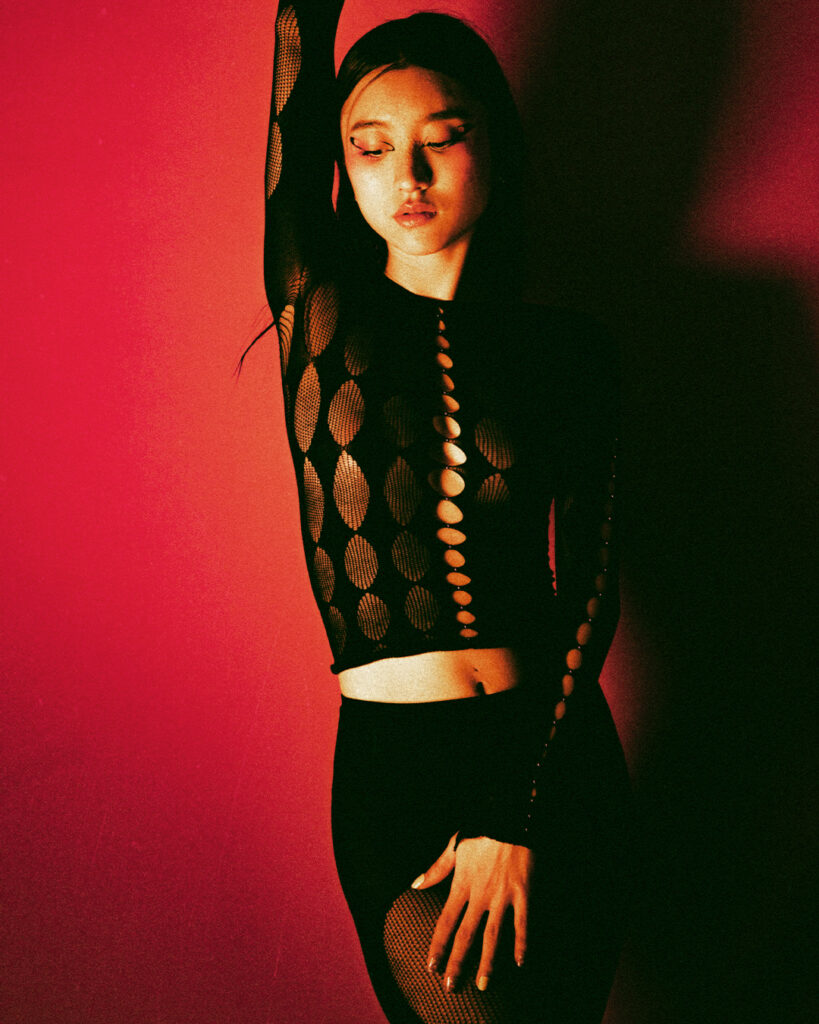
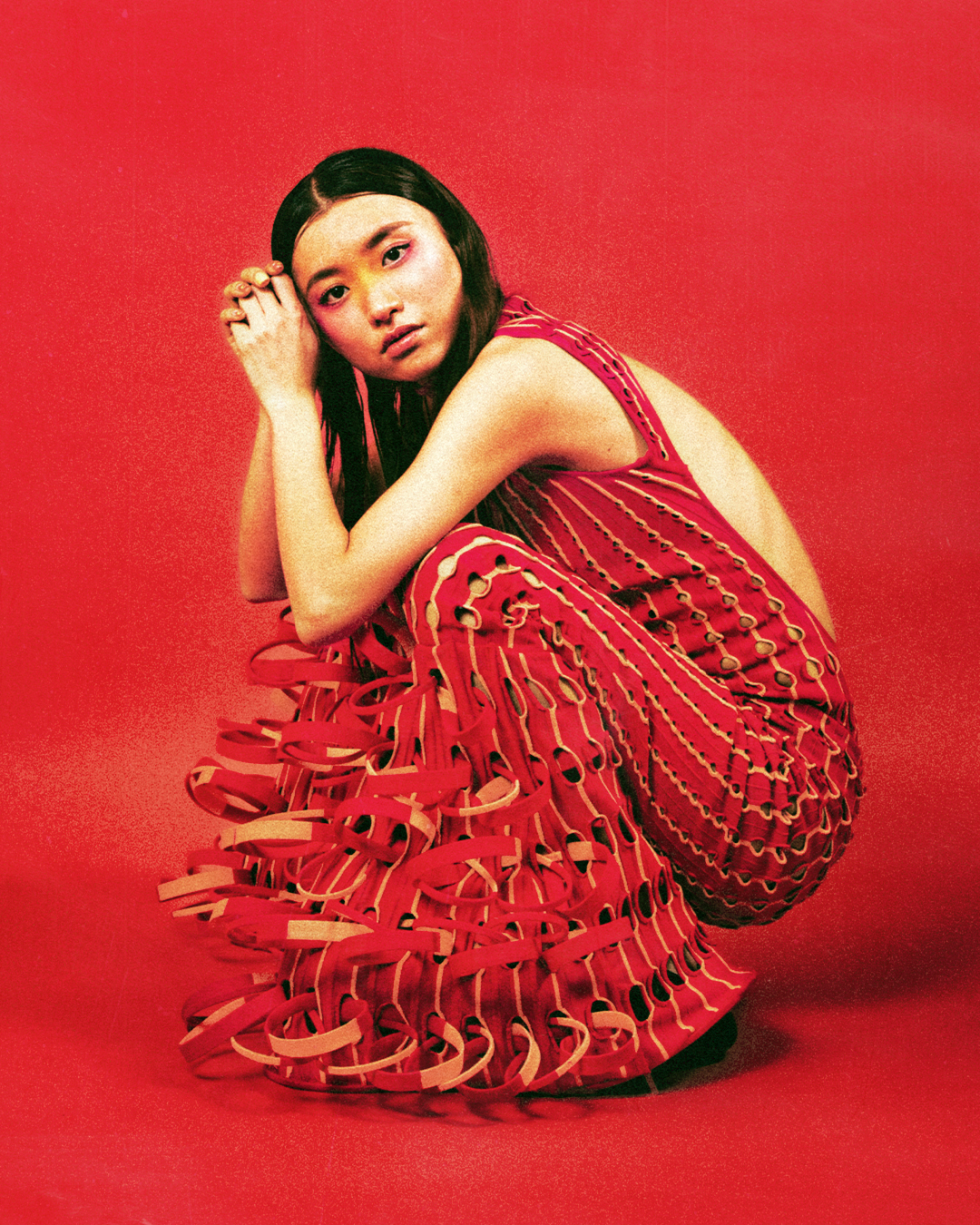
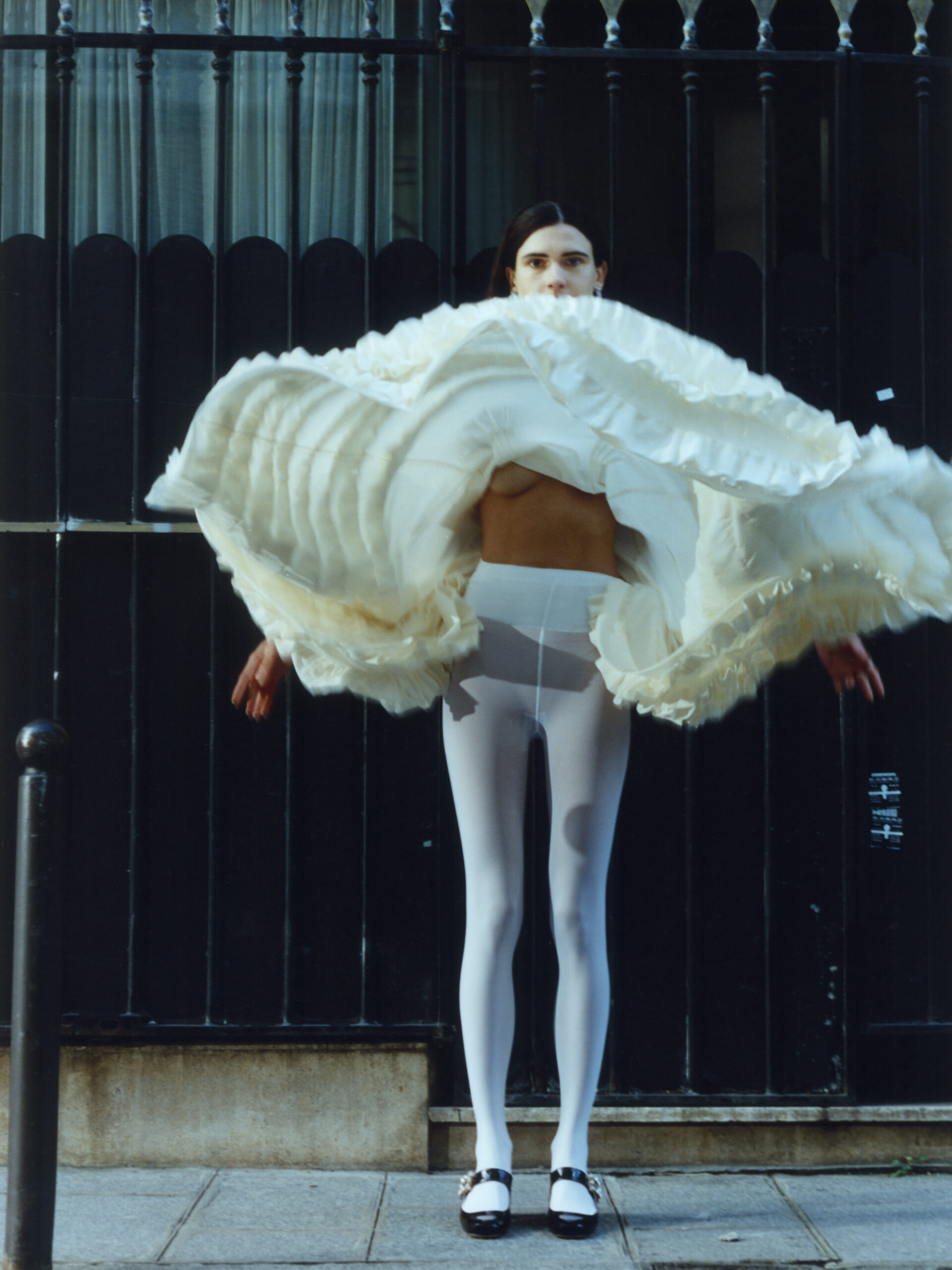
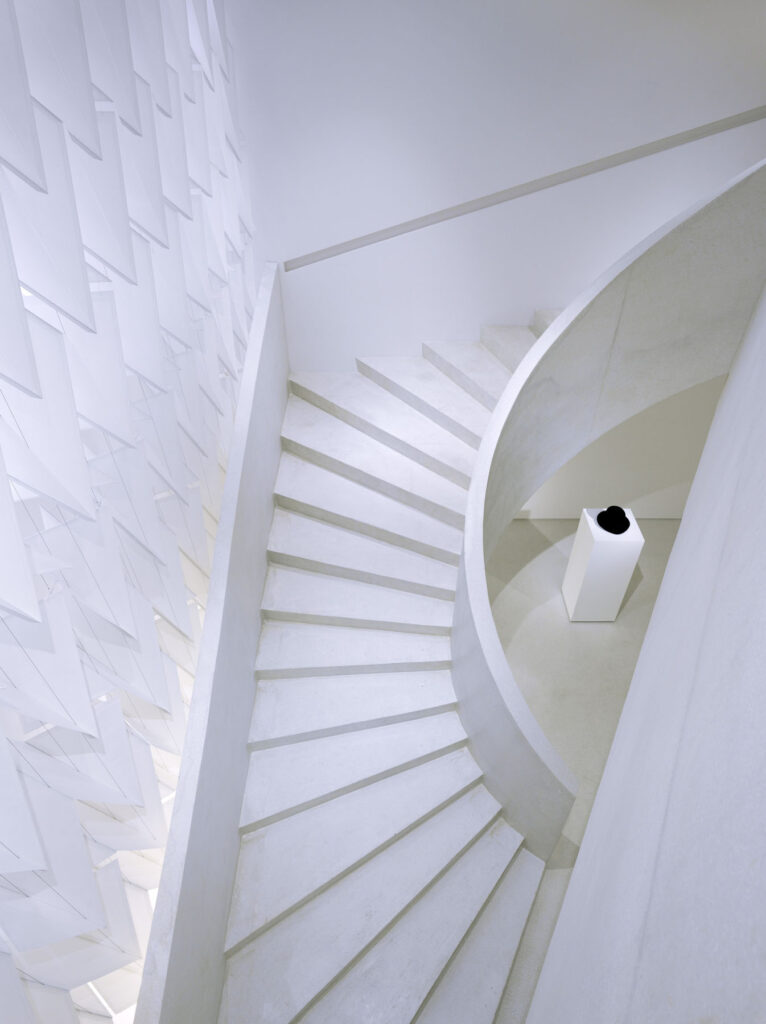
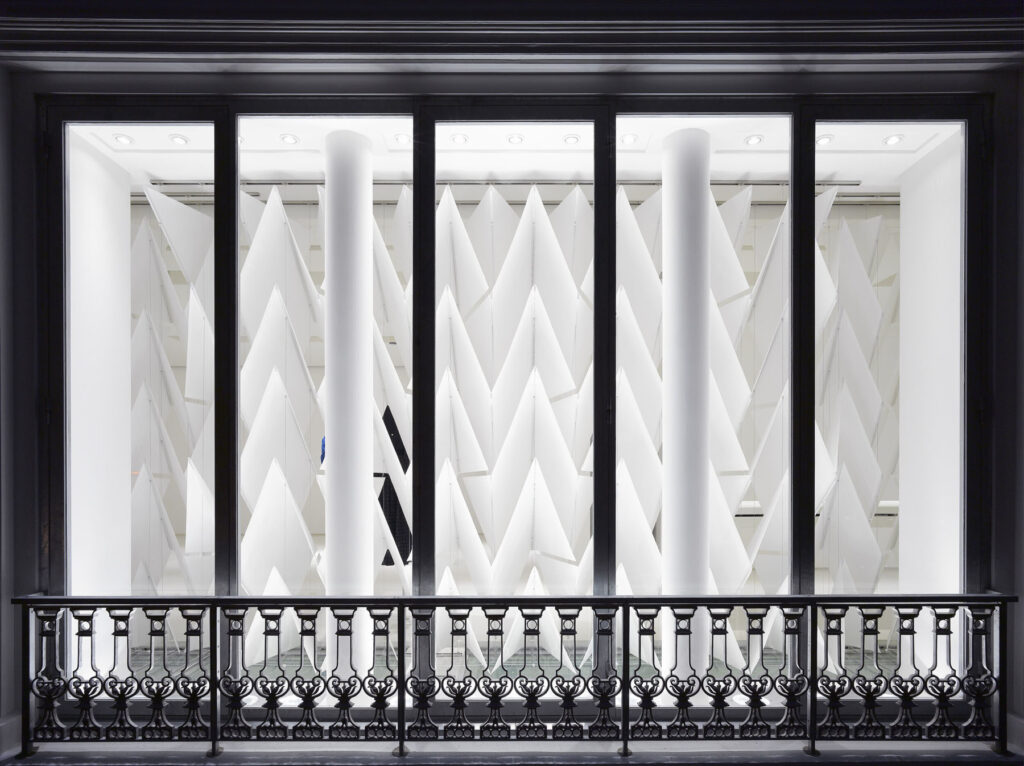
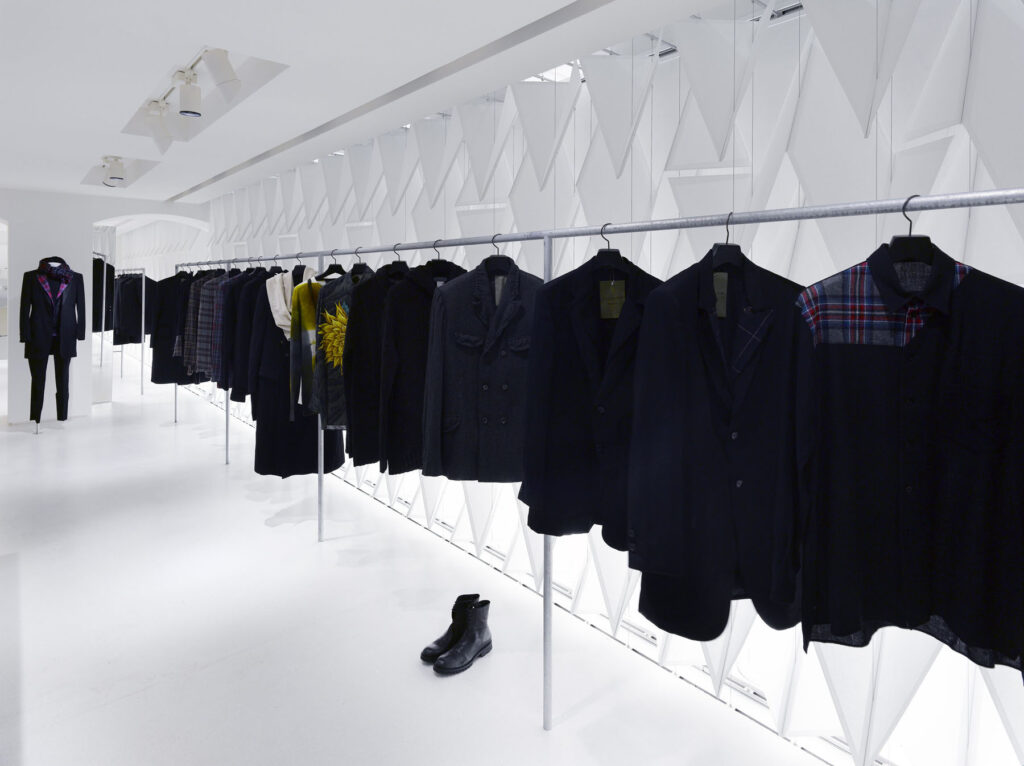
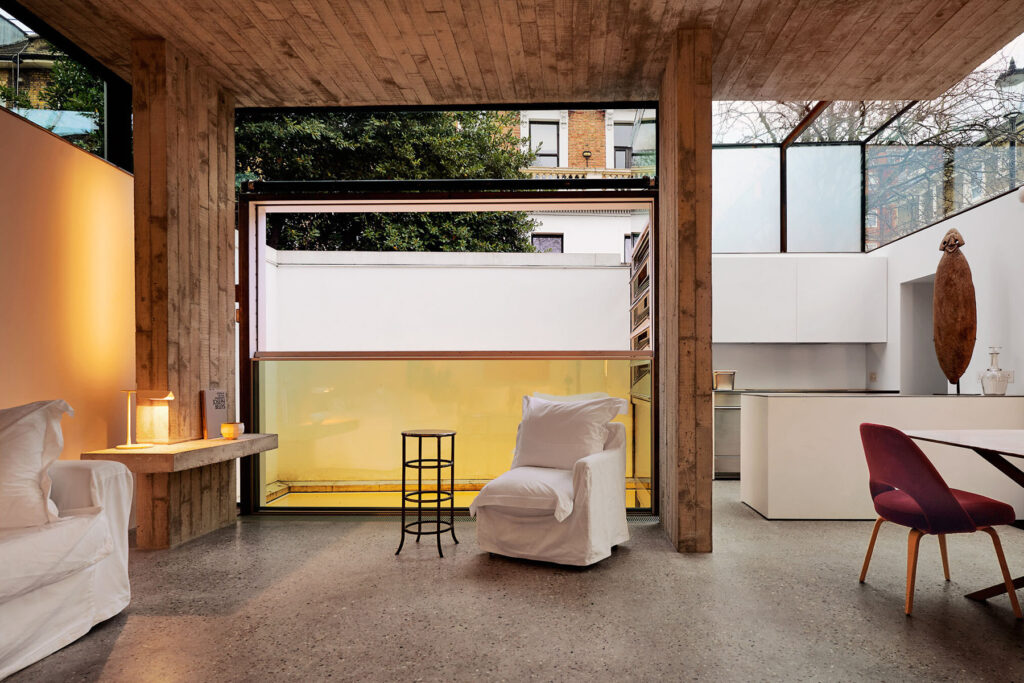
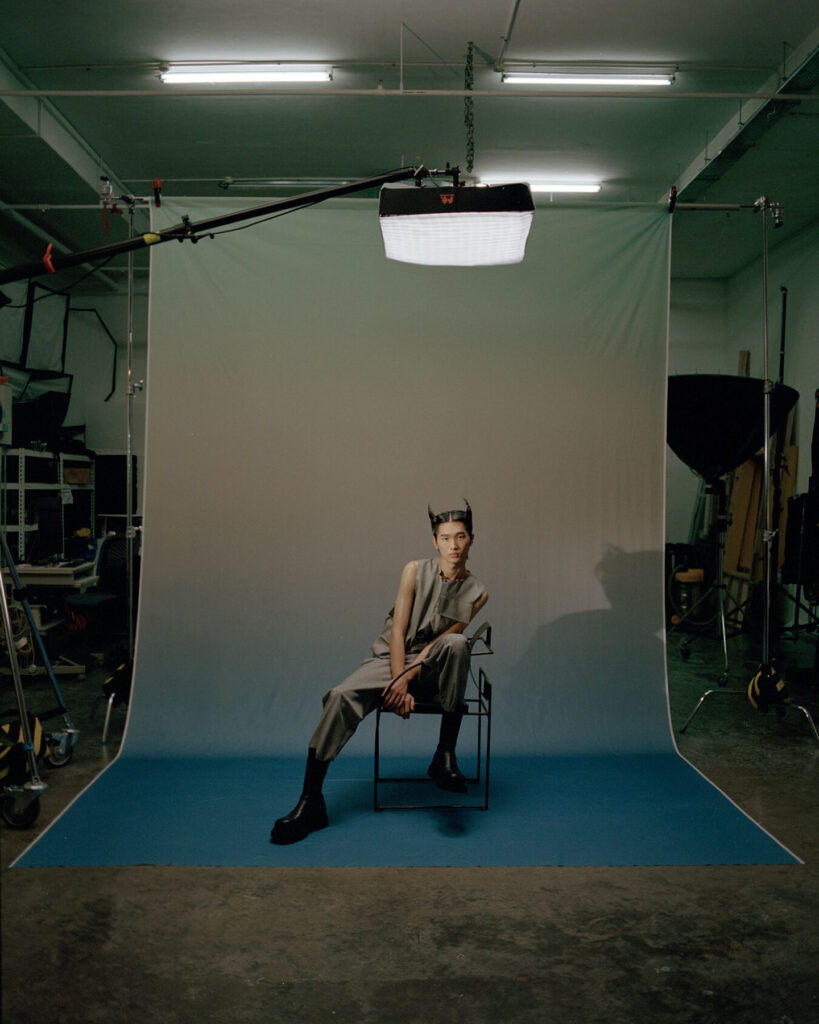
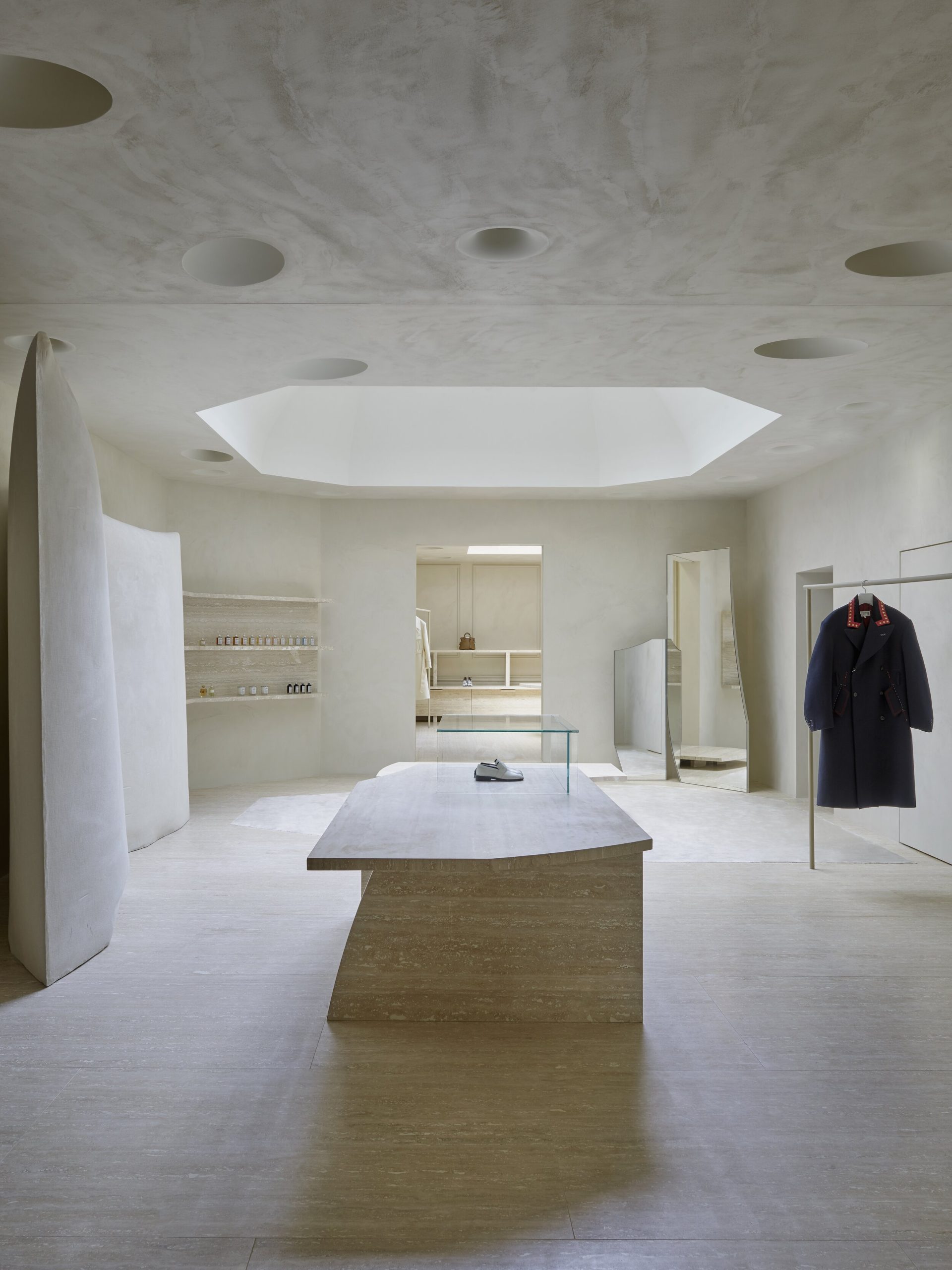
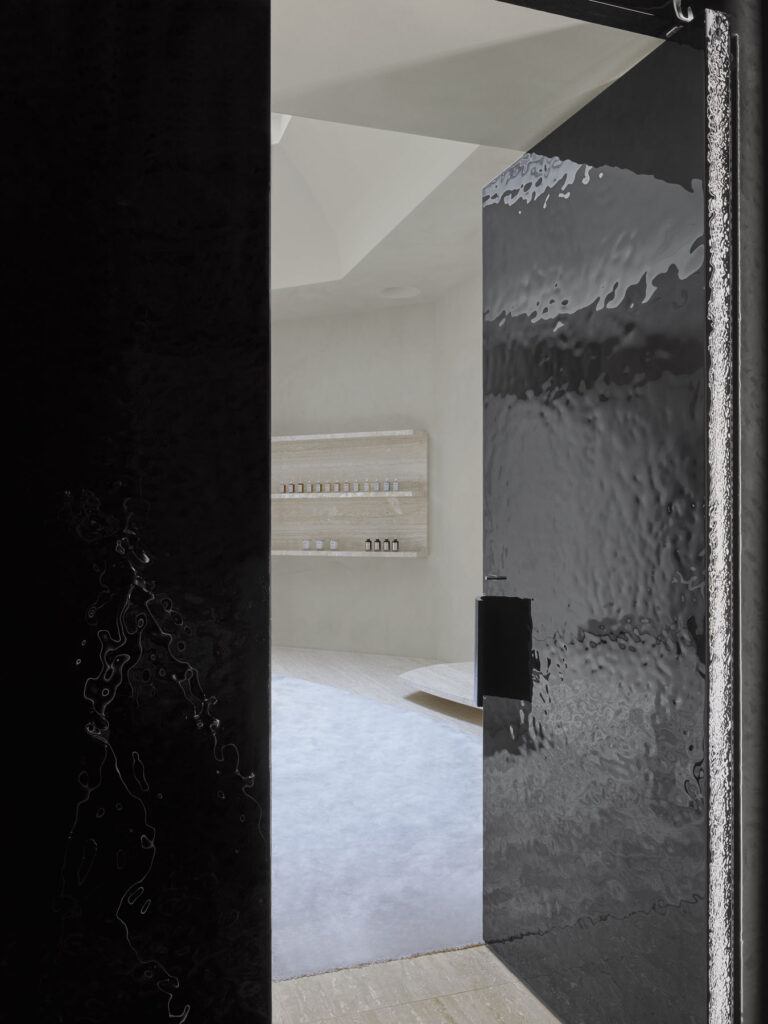
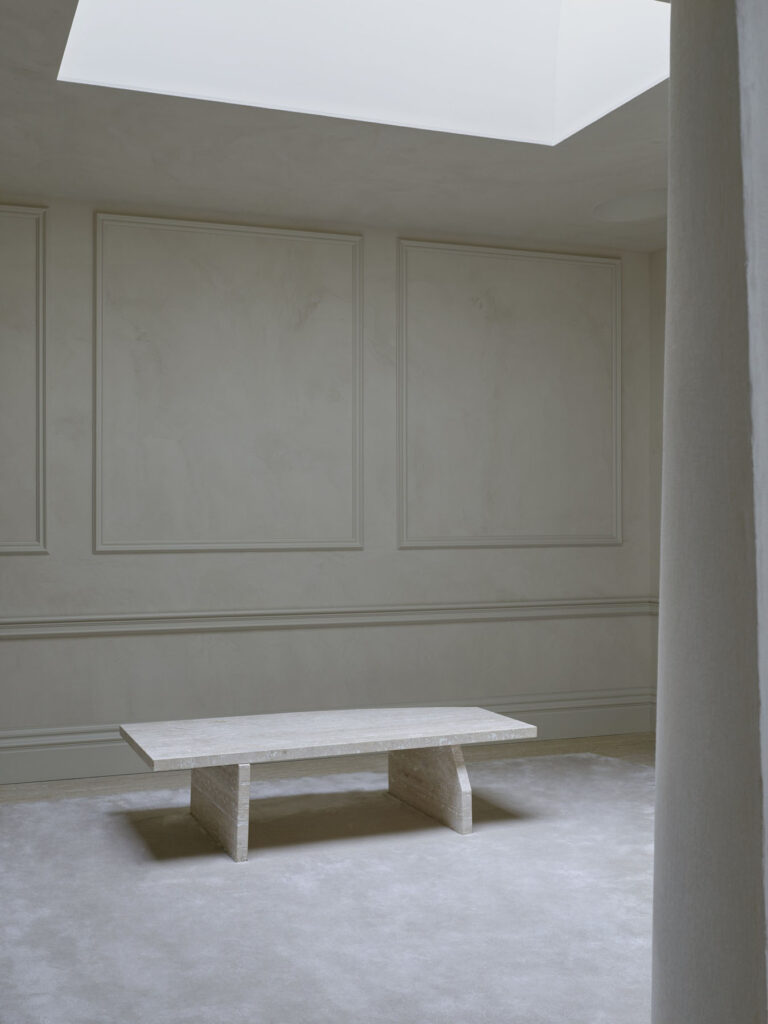
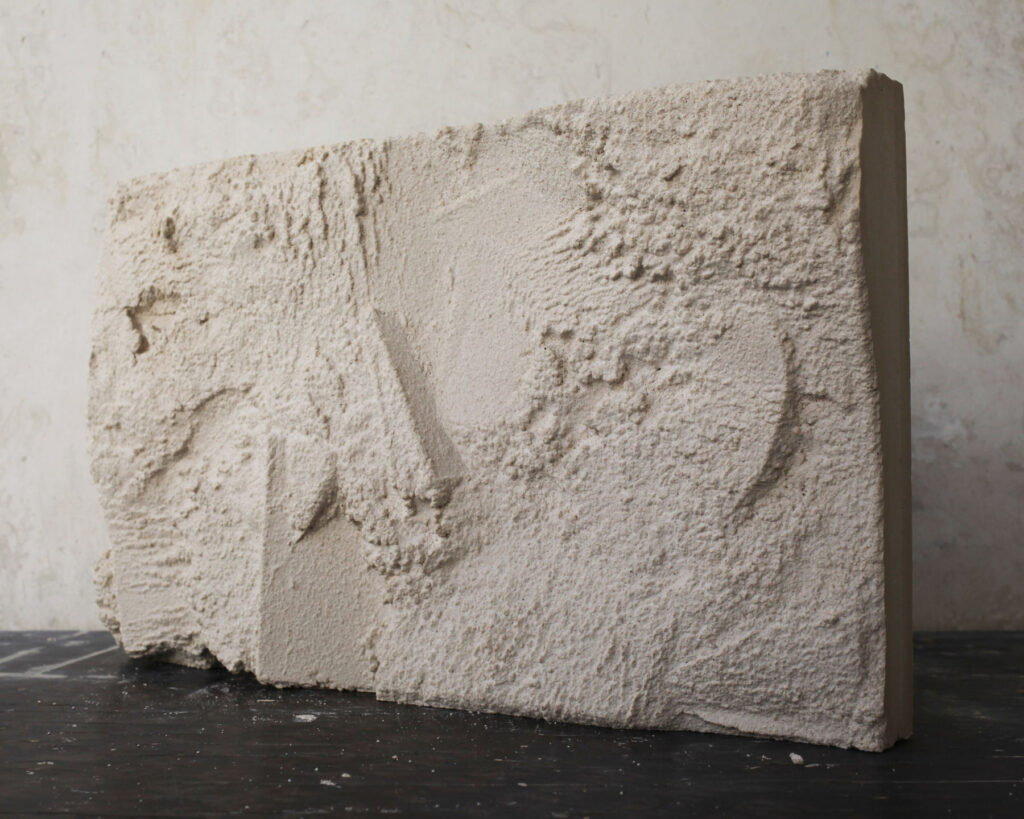
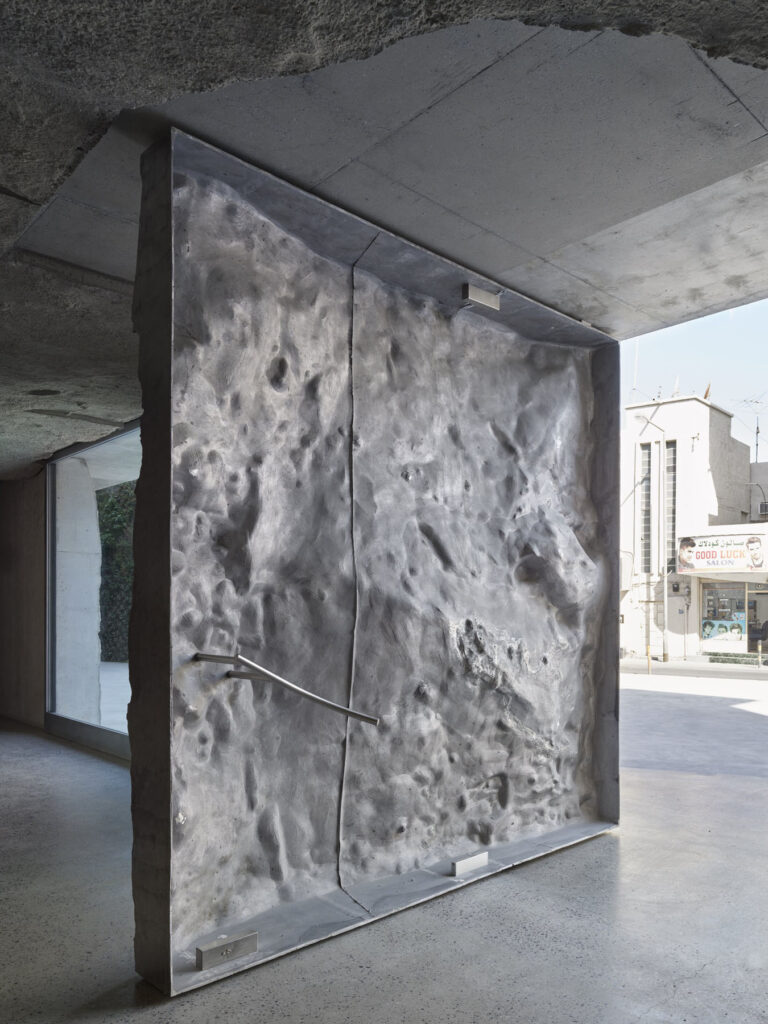
What I really wanted to do was to be creative and to create something myself. With photography and styling photographs, you are in effect, being creative but you’re putting together teams like a director. You’re grabbing clothes, putting together teams of photographers, models, hair, makeup and inventing a story, but you’re not actually taking the photograph or designing the clothes. I’d always been interested in architecture ever since I was a teenager, and I just decided to completely change paths and see if I could be an architect and create things myself that would affect how people experience the world.
Was that scary? The fashion world is such a dynamic and intimidating place to work in. Was it a shock moving into the world of architecture?
Yes. I quite like having new and different experiences, and I quite like taking risks. Towards the end of my fashion career, I was working for Azzedine Alaïa doing a set of photographs with him of his previous collections from the start until that point in the mid-80s. We were recording all his collections for a book that he eventually bought out. So I was dressed top to toe in Alaïa – the tailored pieces, not the slinky ones, but I was pretty sharply dressed. I’ve never been so smart since. I swanned up to the Architectural Association for an interview looking like something they’d never really seen before.
They asked to see my portfolio, and I told them I didn’t have one, only my fashion sketches. In those days at fashion shows, you weren’t allowed to photograph the clothes because they were kept embargoed until they actually got into the shops, so if you were an editor, you sat there sketching in your notebooks. You had to sketch extremely quickly because the models would come by quite fast. I showed them these books, and I was sitting there in a black tailored double-breasted suit – I think they just thought I was mad. I heard afterwards that they really didn’t think I would stick it, but they didn’t realise that if I decide to do something, I do it.
But they offered me a place, and on day one, I knew I shouldn’t walk in there all dressed up, so I decided to go completely under the radar and became unnoticeable. You had to absorb yourself and become a chameleon. It was about the second term, when someone turned to me and asked, ‘You’re not that Sophie Hicks who used to be the fashion editor at Vogue, are you?’ and I said, ‘well, yes, I am actually.’ and she said, ‘why do you look like that then?’ it was all quite amusing. I just really enjoyed drawing and making things. We did a lot of work in the workshops – we would weld, cut, saw, and make models. I loved all of that. We did a lot of expressive drawings, which were pre-computer, and I’m not a good drawer by hand, so I’d make a lot with clay, plaster, carving, printing, and etching etc.
We would talk a lot about our ideas. And the Architectural Association is brilliant at teaching design, and brilliant at teaching you how to think. I’m an external examiner there now, which I’ve been doing for the last four years, and it’s amazing how they get their students to think – to a level that I don’t think you get in other schools.
It’s a bit like if you were thinking about conceptual art, I suppose. Thinking about what the concept is, what the meaning behind it is and why you’re doing it. Absolutely everything needs an explanation when you design, and it’s got nothing to do with aesthetics until you know why you’re doing it, then the aesthetics happen naturally. Of course, some people do their aesthetics better than others – some people have an elegance, and some people don’t. But if there isn’t a reason behind why you’re doing something, then I don’t think it’s very meaningful.
I’ve always thought that film directors have a very interesting job, with the way they approach a project and how they set up a team and choosing all the people who are going to gel as unit. It was Grace Coddington who taught me how to set up a team when you’re doing a fashion shoot. The psychology of a group is incredibly important. I took that kind of thinking with me to the world of architecture: thinking broadly, out of the box and about how to set up an architectural project in a way that is more likely to be successful.
What inspiration do you draw from other engineers and architects – particularly with Félix Candela and Paulo Mendes da Rocha?
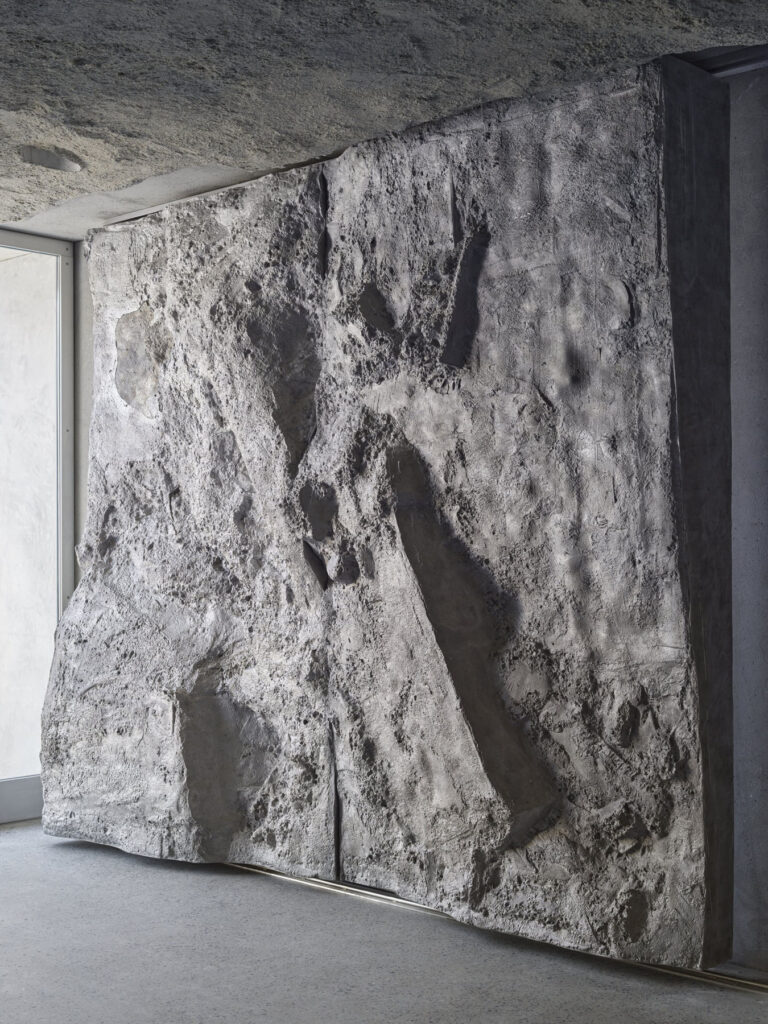
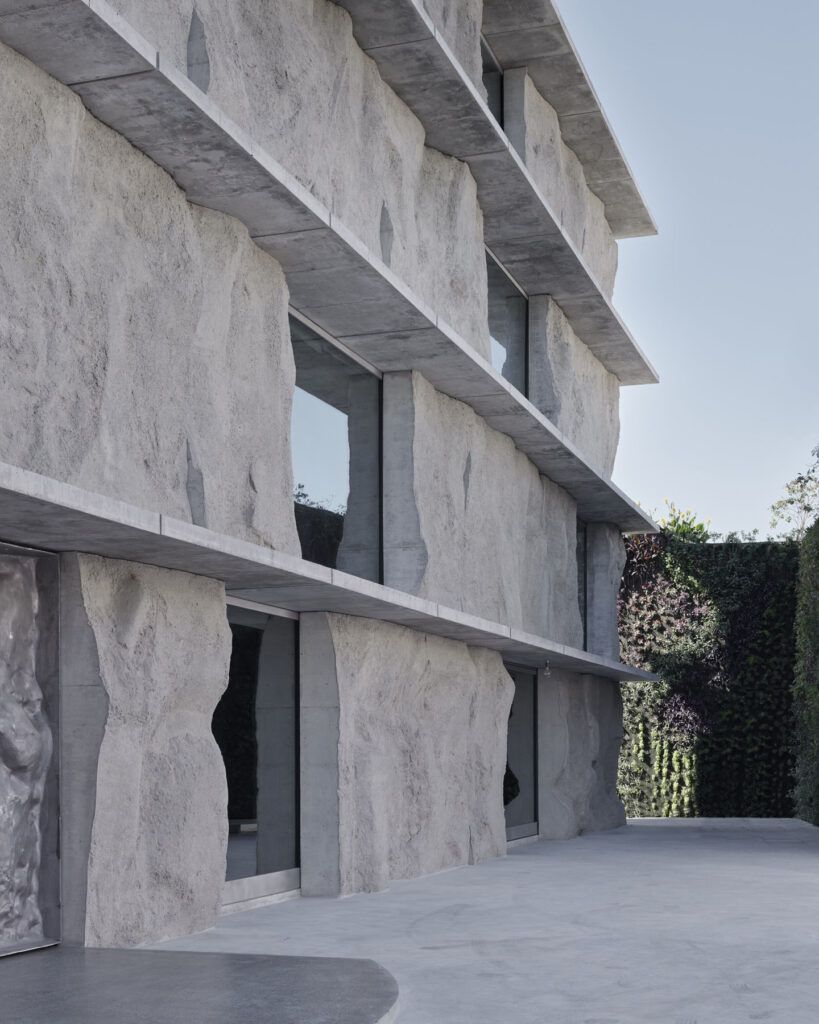
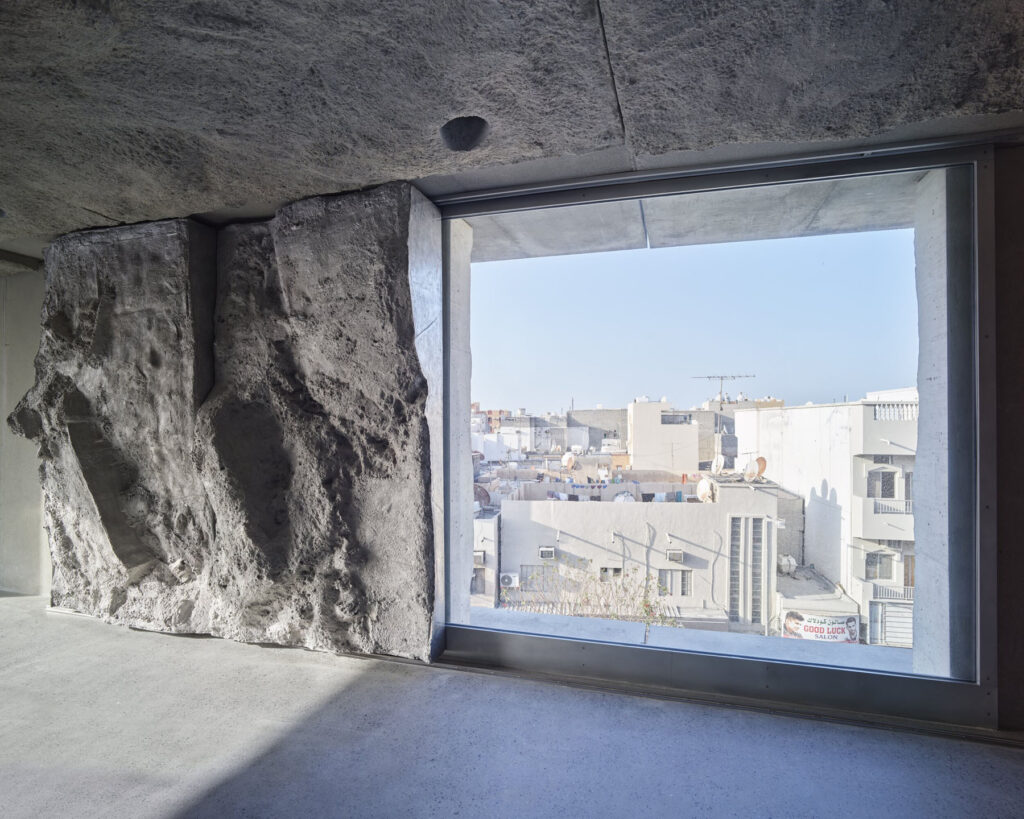
They worked brilliantly with concrete. Recently, I’ve used quite a bit of concrete in buildings I’ve made. I think Félix Candela was probably the most brilliant user of concrete who has ever lived. He mathematically worked out how to create very thin, reinforced concrete shells that were very elegant and incredibly clever. And if you can do something very clever, why wouldn’t you? He also did this because he was designing quite simple structures like bus shelters and churches for communities in Mexico. The budgets were very tight, and I believe he even designed some churches without windows. Because of this low budget, he used less concrete, so the building was less expensive. Because of that, he designed these extraordinary floating canopies and canopy rooves, where the geometry is really his invention. His brilliance as an engineer allowed him to do that. There are some wonderful photographs of this, one in particular which has workman standing on top of this mushroom-like roof. It’s about 10 or 15 metres high and incredibly thin. It’s just a brilliant demonstration of history.
Paulo Mendes da Rocha’s buildings in and around Sao Paolo have an incredible force to them. They’re raw and feel very dynamic, as they have so much embodied energy, in that they are incredibly still. The thing about him which I find very interesting, and which I feel reassured by, is when when I hear about architects of his stature that did what I do, which is having an office of one. An architect of his stature, you would expect to have an office of quite a lot of people, but he maintained a very small office. I’ve never had a big office – I’ve had an office of about 10 people perhaps, and I found that I wasn’t properly designing myself. I was spending too much time looking after other people and checking their work.
Everything froze with the crash in 2008, and I felt like I really needed to get back to basics. What I really wanted to do was design buildings, and what I really wanted to do was actually be the one doing the designing, not passing it down. I’ve got the most brilliant kind of situation now, where I work very closely with my colleague Tom Hopes, and we work very well together. He’s very strong on construction, and I’m very strong on design. He’s teaching me construction and I’m teaching him design – we do both and understand both sides. My aspiration would be to continue to work in this way, and to continue to work in the way that Mendes da Rocha worked. That involved only bringing in other team members for a project when you need to, so you don’t have everyone in the office all the time.
The most recent building I did was a house in Northamptonshire, and it was a reasonably big team. We did all the drawings here, with about 10 or so people, but it worked very well because the quality of the design and the detail was that bit higher. We work very closely as a team and get much better results, I feel. But it’s an unusual way to work, so I’m always encouraged when I read that someone like him created really interesting buildings with that same process.
What do you value most about a living space?
That it’s really comfortable, and not just literally. It’s important that you feel relaxed, calm, and able to be yourself in and around it. The word ‘comfortable’ might have the wrong connotations because it makes you think about sitting on squishy chairs, but it’s not that. It’s a kind of feeling – feeling yourself.
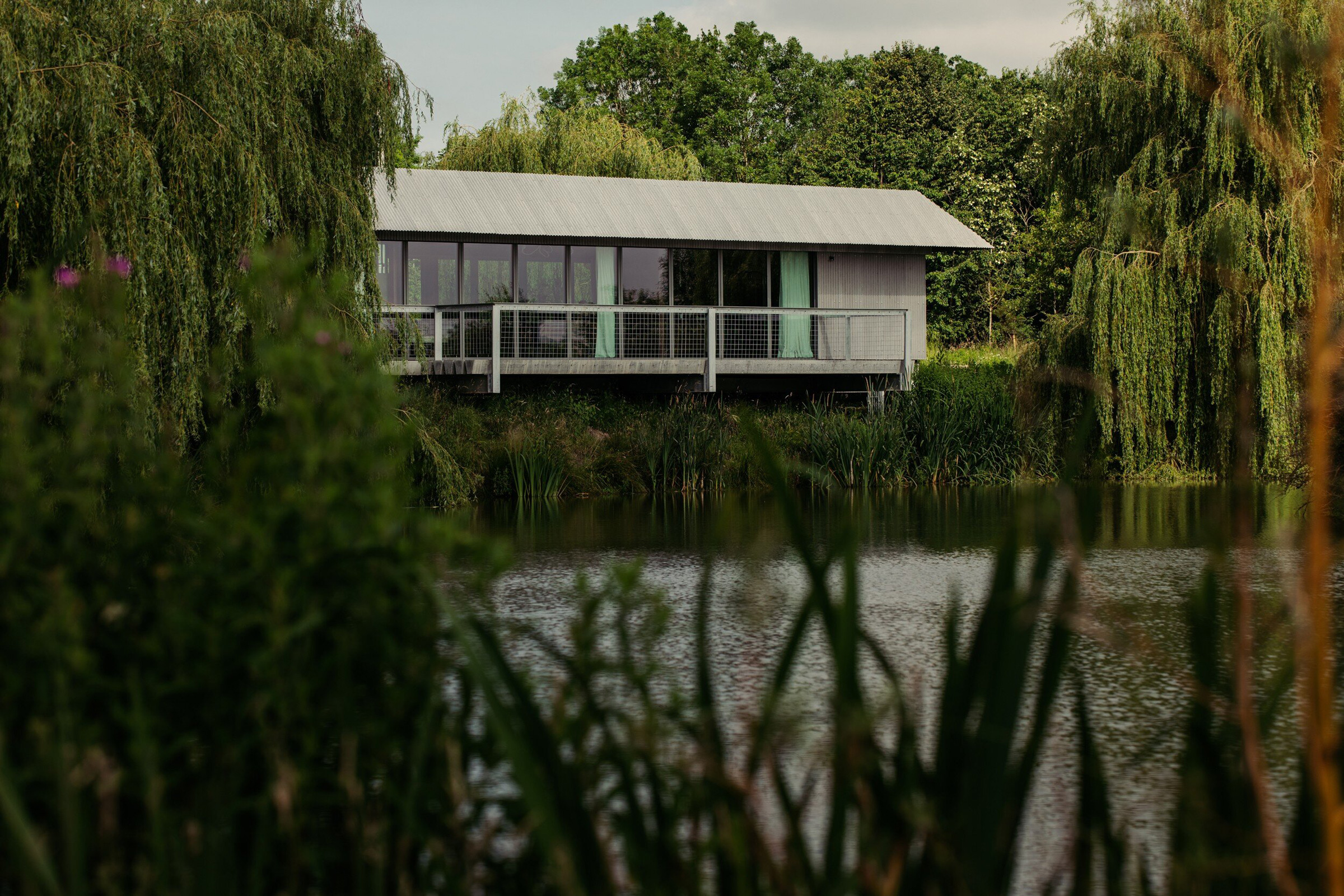
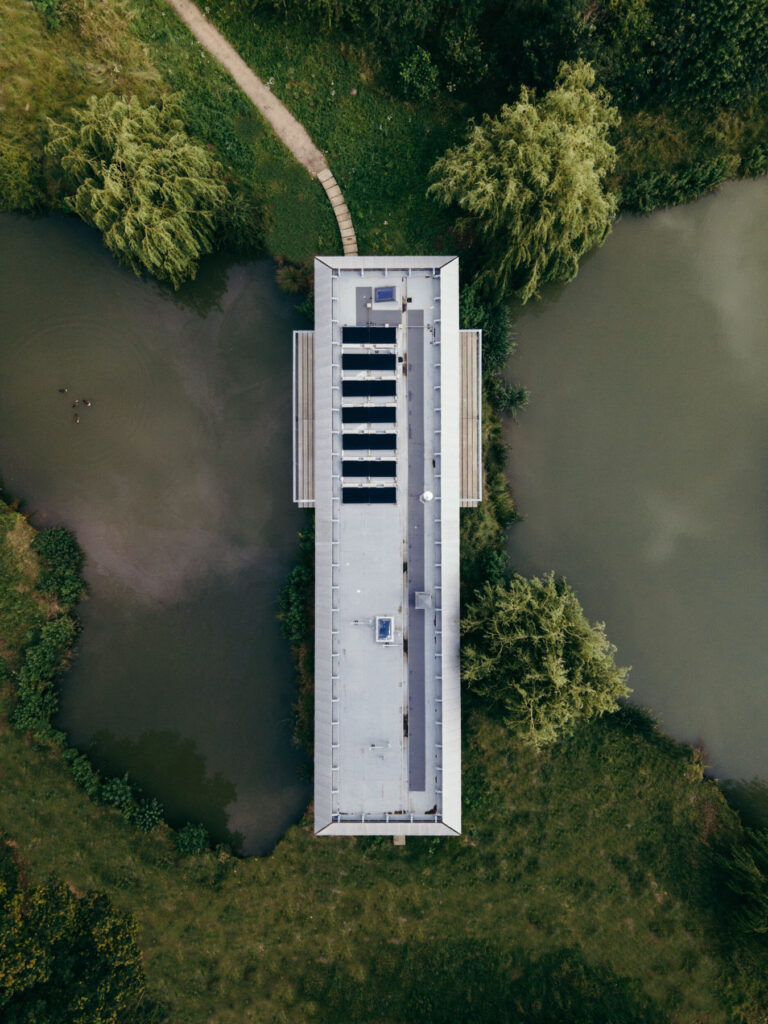
When I design for other people, I want to find out what makes them feel right. If I’m designing a house for somebody, I want to know everything about how they live, how they behave, what makes them feel comfortable, and what kind of impression they want that building to embody. With the house that I designed for my daughter recently, which is called House Between Two Lakes, it was really important to her that it wasn’t a show-off-y house. She didn’t want a flashy house. She didn’t want a house that was obtrusive. She wanted something that was the opposite of a designed house, which is why we made something that sat very gently in the landscape, and that is very streamlined.
As the theme of this issue is identity, I thought it would be interesting to know if you’ve ever had kind of ‘identity crisis’ with a project?
That’s a difficult one, because architectural projects are very long and very complicated, and they involve an awful lot of solving problems. These problems might be thrown up by the environment or by the building problems that crop up during construction. If you’re working on a project where you’re solving problems, an identity crisis is less common.
There’s initial design that you tend not to go forward with until you’ve got the concept sorted out. Projects don’t go ahead if you can’t get that right. It’s a difficult question for me to answer. I know it sounds as if I’m not admitting to self-doubt, but that’s not it. As an architect, you’re a servant of the client, so you need to understand what they’re all about. If you don’t understand what they’re all about, the project tends not to go forward. If you are trying to understand what they’re all about, you carry on until you reach a point of agreement, and during that process, there are often moments where you doubt if you’re ever going to get there. There are multiple points in time where I would be searching for the solution that would embody the character or the ethos of a brand, or the character of the person or thing that they want to embody in the building. It might be some sort of feelings or atmosphere, and I might be struggling to understand what they really mean. And even when I do understand, I have to then find a way of translating that into a built form.
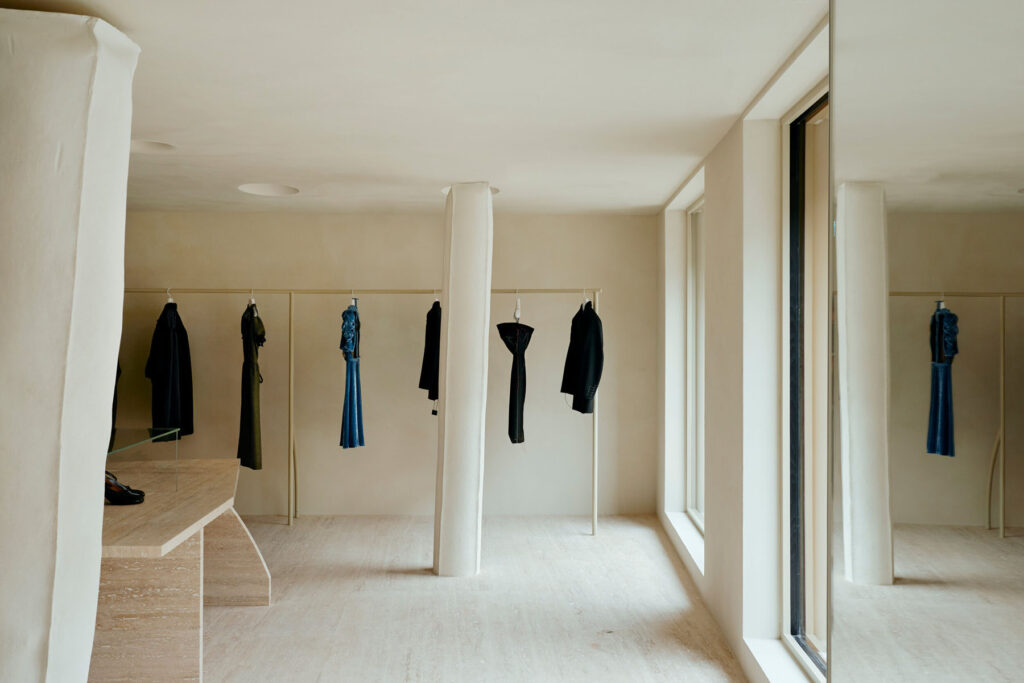
There is a kind of lightbulb moment when you get it right. It happened with the Chloé shop early on for Phoebe Philo. I was struggling with what to do for this luxurious brand, and for its new, young, dynamic designer. She’s got great ideas and a contemporary way of looking at things. At the end of the day, it’s a Paris luxury house, and had stores on fancy shopping streets. I thought about what we could do to bring the spirit of that young designer into the shop environment in a way that would feel how I think she feels about her designs. I really thought we weren’t going to get there. I really didn’t know what I was going to be able to suggest, and then suddenly, we had riots in Bond Street. There were some demonstrations, and the shop fronts were boarded up, and that was my lightbulb moment. We used railing and raw plywood like you would use to protect your front window. We put that inside the shop and used it as the finish for the walls. There’s a real beauty to basic plywood. Not fancy plywood and beautiful veneer, just the bog-standard shuttering with lots of faults in it. I wanted to bring that into this luxury space and offset it with the pink marble and gold-plated metal fittings that Phoebe was working on. We gave it a kind of spin that would tell the kinds of rich women who are going to come into shop, that there’s something else going on here. The spirit of the place is just a bit more rooted in reality.
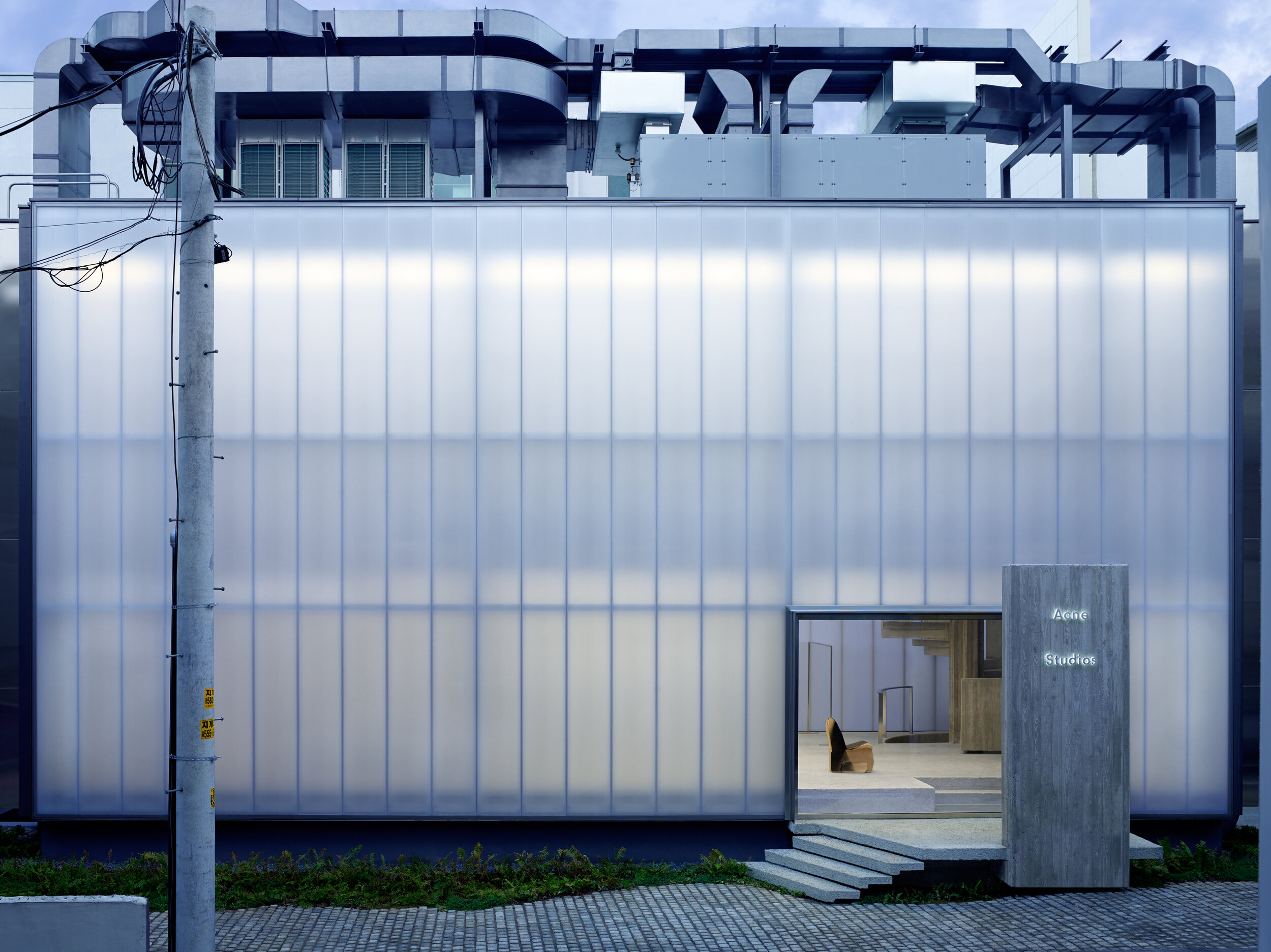
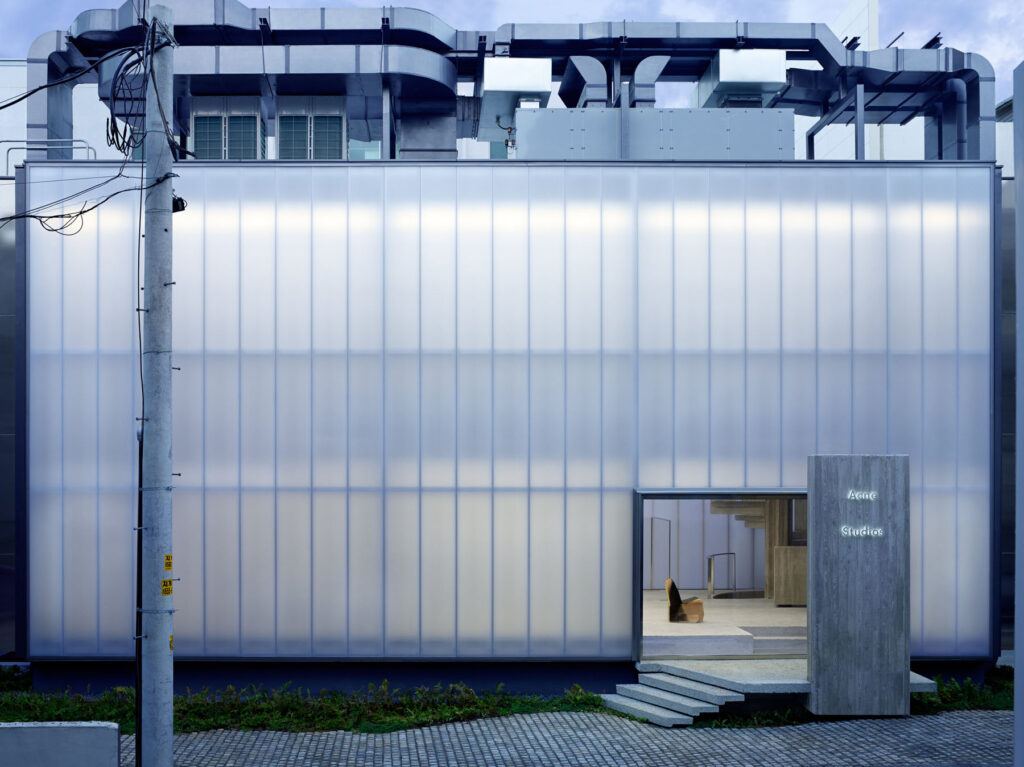
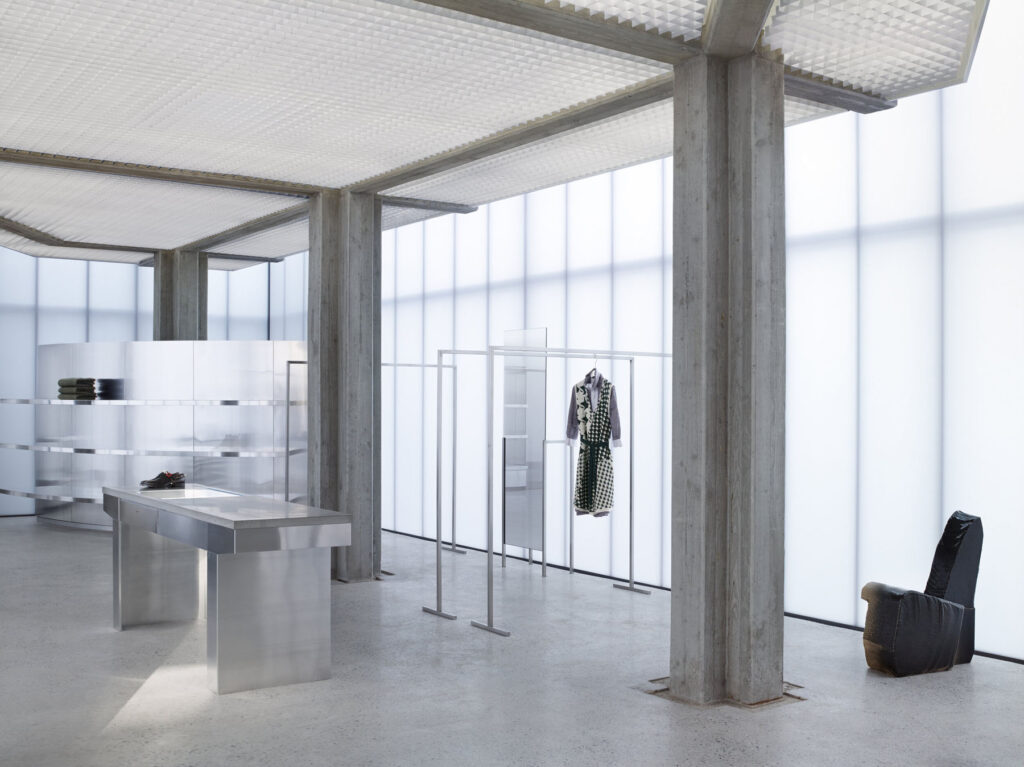
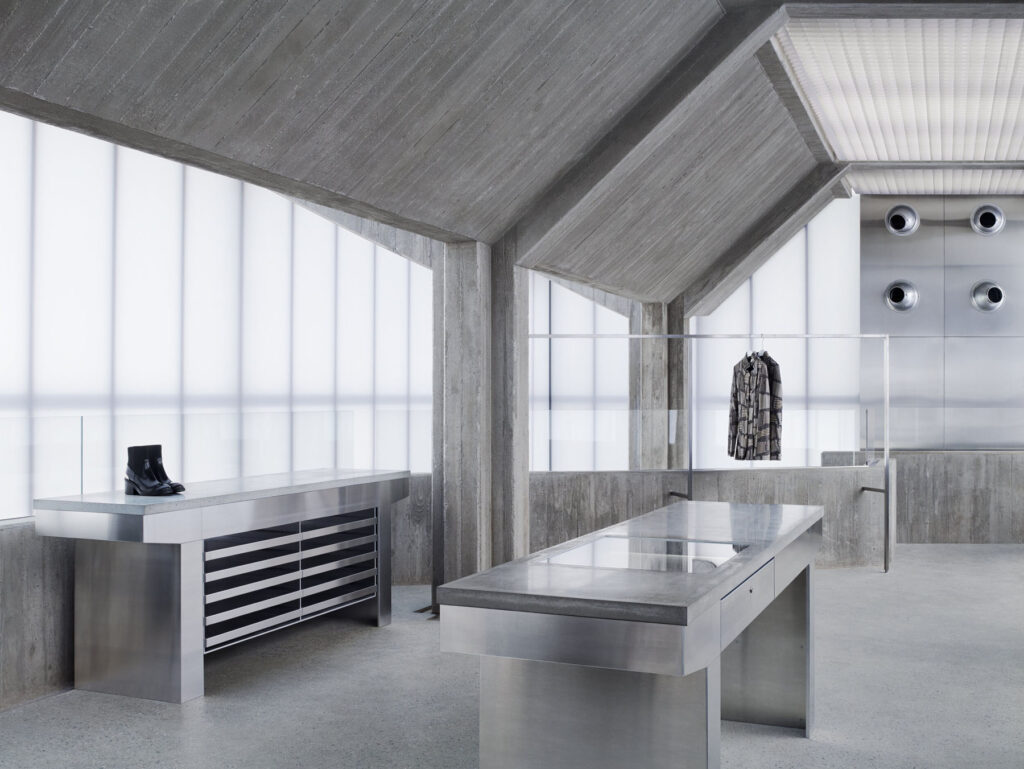
Your Acne Studios flagship store has a very forceful and distinct presence, reflecting the studio’s designs and aversion to conventional Swedish design. What were the other influences behind this project?
When working with a fashion client or a brand, they have very distinct characteristics and their brand identity is important to them, so it’s about finding an architecture that will embody that character and ethos. When I have a new client, I go and study that person, or that group of designers.
I’d never been to Sweden before Acne Studios contacted me, so I spent a long time shadowing Jonny Johansson during design meetings, hearing how he spoke to other people and absorbing how he works and how he makes his choices. I also spent quite a lot of time travelling around Sweden and going to the islands to gather information in my mind about Swedish light.