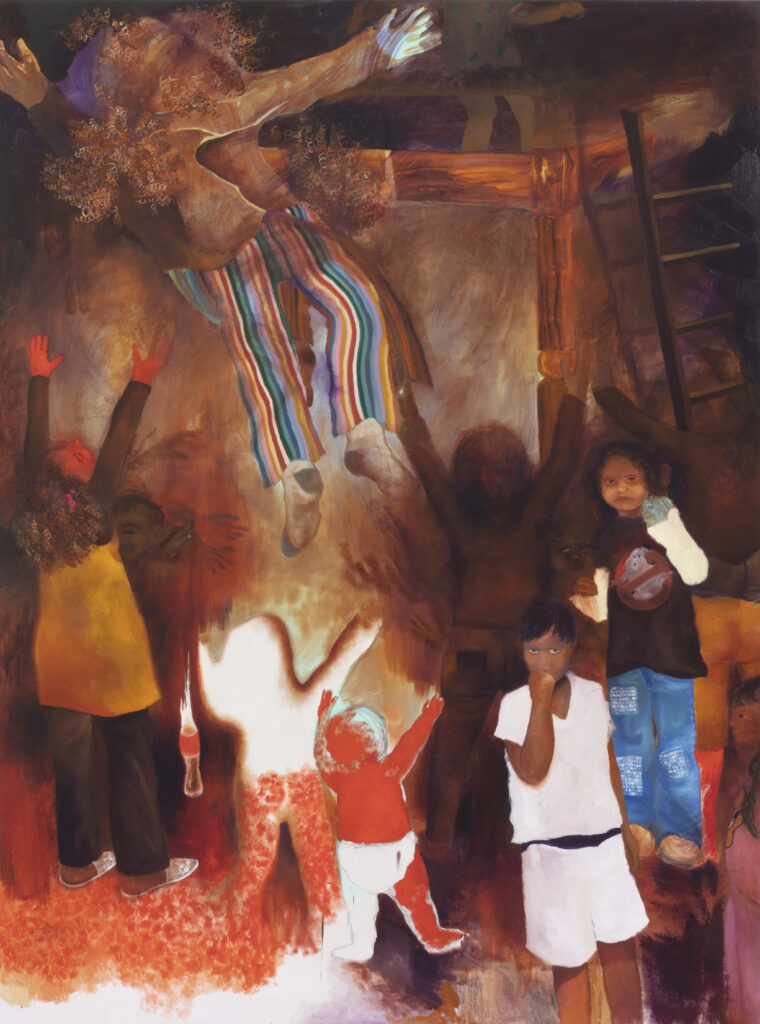House Of The Pink Spot, Non-Negotiables and Banishing Egotism
Frankie Pappas is the collective pseudonym for an international architecture and design firm based in South Africa. They describe themselves as “a collection of brilliant young minds that do away with personal egotisms to find remarkable solutions.” NR Magazine joined Ant (I’d rather you didn’t use my surname please) in conversation. Ant is a storyteller, each question revealing more about the work of Frankie Pappas and the ideals and motivations behind the firm, each more interesting and radical than the last.
Nicola Barrett: What was the process behind the creation of House of the Pink Spot and what were some of the challenges you faced on this project?
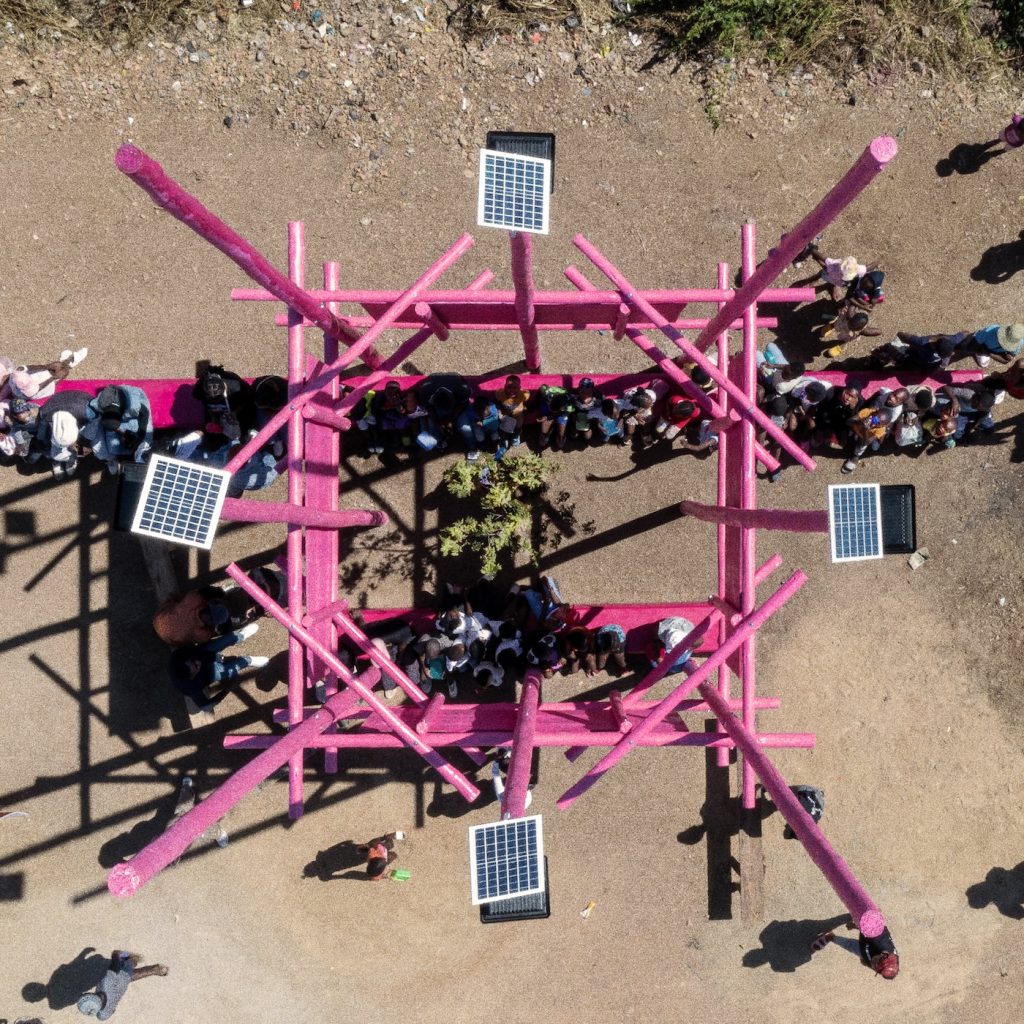
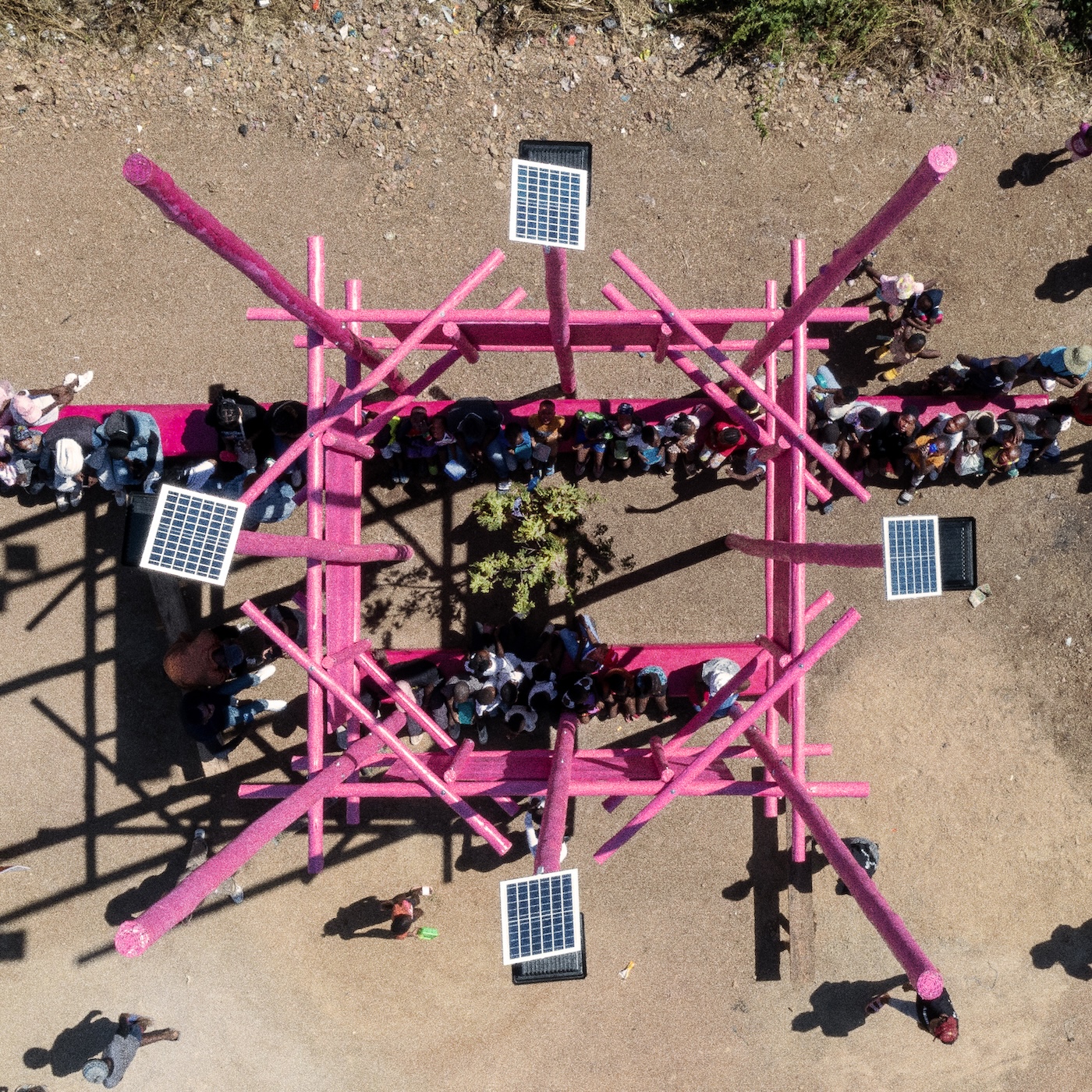
That building came about because a friend of mine, Alicia, heads up this thing called Digital Disruptors. It’s one of her many projects. She wanted something to do in this area, Orange Farm, Drieziek in Johannesburg. She’d gotten some money and she didn’t know what to do with it. I said, well, I would approach it from an architectural perspective. I’m fascinated by how you can make small interventions in parts of the city and see what impact they have.
There are two stories that I told Alicia. One was of Guatemala. They were having these huge drug wars. I went there maybe ten years ago, just after these drug wars had kind of been quelled a bit in the urban areas. They were trying to reinitiate the use of these public spaces. So they just put massive amounts of really fast WiFi into these public places and a lot of light. When I went there these places were so full, everyone was working in their laptops. It was quite amazing. This idea that once you initiate people into a space, it inherently becomes a little bit safer.
Another story like this that I like, is in Kenya, there is a main road to the airport that is incredibly well-lit. The reason is that the government wanted its dignitaries to have safe passage to the airport and back. I saw this one photograph, and it just stuck in my mind. It’s of these school kids sitting along this road, miles and miles of them because this is the only light they have access to. Doing their homework. And it was just amazing.
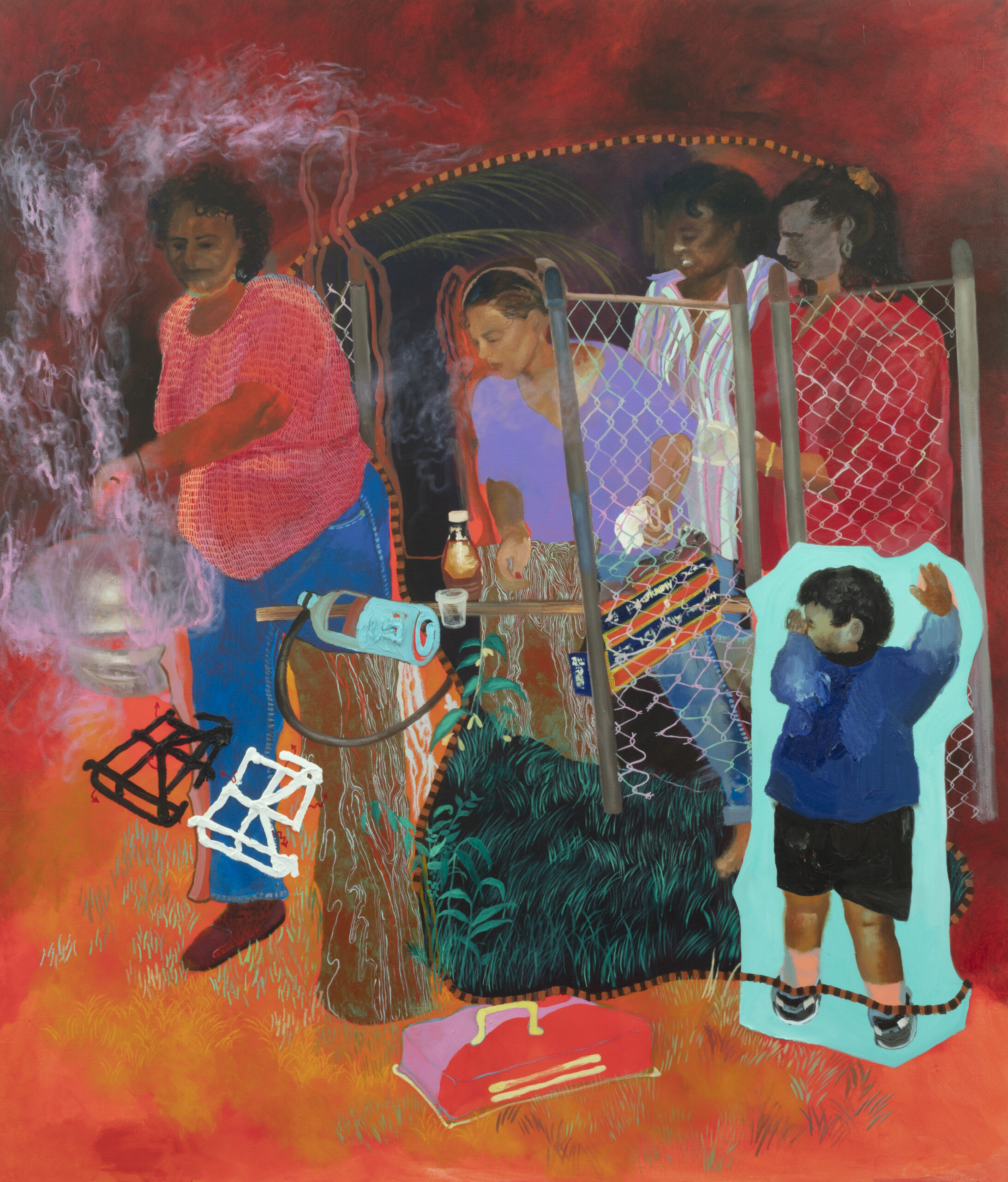
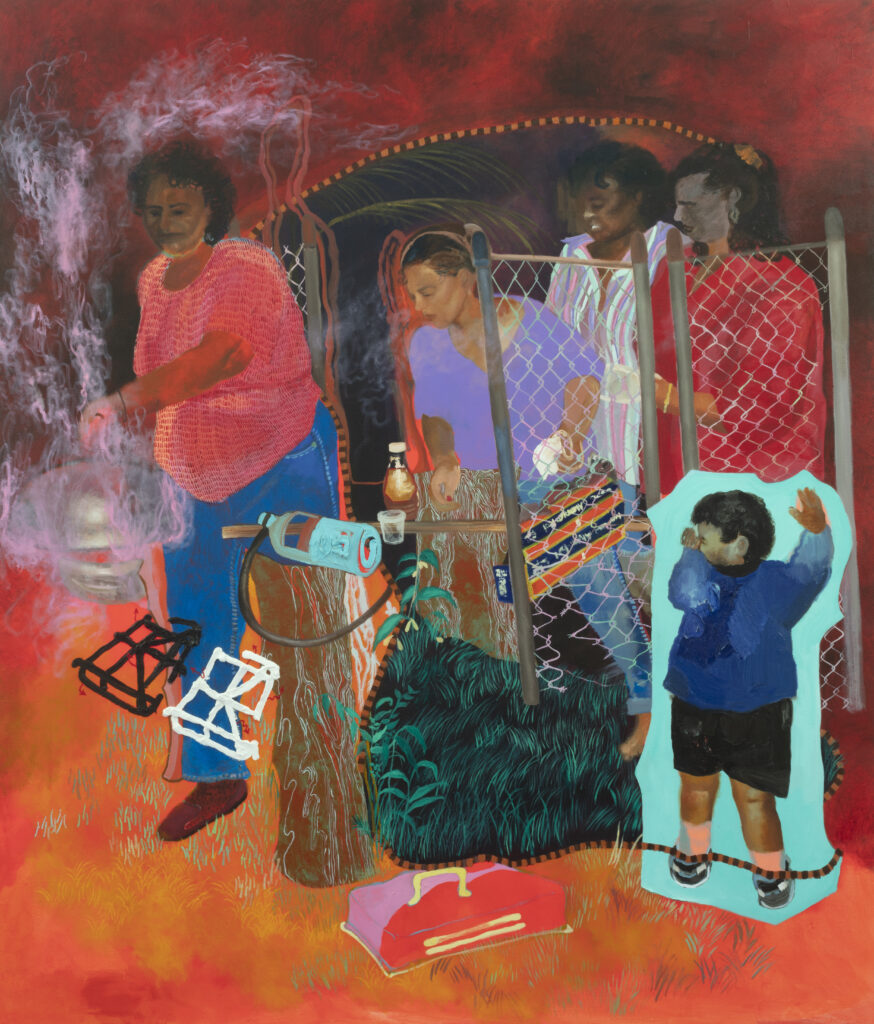
These two things stuck in my mind. I said, Alicia, this is probably what I would try to do. Bring light to the space and a hell of a lot of WiFi. Let’s find a spot where this could work. When we were there with GBV survivors and activists, they chose this one spot which was a dumping ground. We got that cleaned up and in essence, built this public park. I mean, it’s very small, but that’s what we had available in terms of the fund. We worked for free on this project because the budget was so small.
The construction of it is really interesting. It’s got to be the tallest building in Drieziek. We ordered the longest telephone poles we could get our hands on, painted them pink on the ground and then hoisted them up with solar lights on top of them. The seating is all just brickwork. It’s very simple stuff. All signage is hand painted by everyone.
The challenges are numerous. The reason why it’s the Pink Spot is because we didn’t want it to be affiliated with a political party. The ANC, which is the ruling party, their colours are green, yellow and black. We went through all the colours of the parties and we were left with purple and pink.
Nicola Barrett: Was it built on private land or public land?
Oh, my word. You’re going to get me into trouble here. I have absolutely no idea.
Nicola Barrett: Did you not come up against opposition when you start building in unclaimed places?
Well, it’s obviously someone’s land. And by someone, I mean, it’s some state enterprise. So it’s definitely not private property. Let’s call it municipal land for the sake of this conversation. It’s municipal land that is not only being under-utilised, it’s not being maintained. It’s a dumping ground.
Surely the city’s land belongs to citizens. I would expect that to not be a controversial statement. But it is. It’s on the bottom of a street that these activists live on. It is like an inherently unsafe space because it’s not being maintained. They said we’re going to try and make it safer for ourselves. We want a way to activate it, to maintain it. All we ask is leave us alone so that we can. Because our governments are so ineffectual, it has to be done by people who care, the citizens. It is like a type of guerrilla architecture.
Nicola Barrett: There are many unused spaces, particularly in urban areas, what’s your opinion of more radical ways of reclaiming these spaces?
I can only speak to it in a South African context. But I’m always surprised at the amount of legislation in the way between what exists and what I would like the city to be like. The offices that I’m in at the moment, this is our first development, because exactly this problem that you’ve spoken about. What we are doing is not by the book. We’ve taken an Apartheid-era house that was not being utilised and we converted it into these six tiny little offices. It goes against every single regulation.
But there’s a market for small office spaces. The smallest office space we can get is 45 square meters. Do we need 45 square meters? No, not really. Then we still have to pay for heating, for lights, for WiFi. Why don’t we do one ourselves where we make a seven square meter spaces and we make five other office spaces for other people with a shared boardroom and we get this thing off the grid so it’s on solar? We don’t need the municipality at all.
If you don’t have the capacity as a citizen to change the city, I mean, what are we doing? I use the word citizen very deliberately because you choose to live in a city, so truly you should be able to change it in some way. It’s liberating, I suppose, in a weird way, to live in South Africa, where the protection of the law is so bad that you can implement this thing that you want to do.
Nicola Barrett: In what ways do you think people with fewer resources could potentially reclaim under-utilised spaces?
This is one of the problems we’re trying to solve at the moment. Providing better accommodation and still making it economically interesting. Think £250 for two-bed apartment. That must sound insane to you. But is that achievable? Can we do it? Yeah, I think we can. It means finding spaces that are under-utilised in the suburbs, that’s easy enough to do because you have garages that are not being used. You’ve got people who are 65 years old who have a four-bedroom house whose kids have all left. Utilising those unused spaces could be done very well.
But the Gherkin can never be done well. In no world is that floor plan divisional. All it supports is big companies. It’s revered as this great piece of architecture by Norman Foster, but it’s a piece of nonsense. But it’s one of the things that’s so frustrating about the architectural world because it’s all about houses for really wealthy people, or big office buildings or the Line. But something like the Pink Spot, I think is a far more interesting project. If you build the Line, you will never be able to change it if you have a normal salary. The way to do it is to parcel land into small enough quantities that normal human beings can create change.
And for architects to get involved in the curation of the city. You cannot be the servant of the rich and you cannot be the barefoot philanthropist, that’s the world. The role of the architect, I think, is looking after the health of the city. And so therefore, as an architect, you should be in the role of apportioning capital to projects that you think are valuable to the future city. The city you’d like to live in, as doctors, should be responsible for looking after the health of humans. Right. But we should afford architects this opportunity or this role. But of course, it’s not done that way. The people who are producing the city are developers who are, in essence working for provident funds or some sort of big capital-allocating entity, and that’s chaos.
Nicola Barrett: House of the Big Arch was designed with not only humans but local wildlife in mind. What were some of the challenges you faced doing this?
I learned to say what is the non-negotiable. And a non-negotiable can be so philosophical and unattainable and unachievable in the beginning and then as long as you don’t move that line, it’s achievable. Can we build this building in a forest without disturbing a tree?
When you produce this very strict problem set, which is; we can’t disturb a tree, we have to get the materials from the closest town, it has to be all be carried by humans. How do we manage these extreme temperatures of 40 degrees? All of these are these very strict parameters that you can’t ignore. And once you are clear about them, it’s almost like linear programming, except not two-dimensional. Like a multidimensional linear programming problem where the problem space is so small that the form produces itself.
This architecture is not a function of invention, it is a function of discovery. Deciding on what those parameters are, that’s the real work. The rest, it just solves itself. Be real about what the problem set is and solve for that. And then you won’t get something boring. Not possible. I’m glad to say that’s the one thing I think all our projects, whether furniture or buildings or artwork, have that in common. Wonderfully similar but beautifully different. Because nothing looks the same. You wouldn’t think House of the Big Arch and House of the Pink Spot and House of the Flying Bowtie are designed by remotely the same people.
Nicola Barrett: So you state that your collective pseudonym challenges the status quo. How so?
This was a joke. That statement is not a joke. But this was kind of poking fun at architecture firms named after the person who owns them. There is this inherent ego in it all. And I find that laughable. For multiple reasons. First of all, like, you have an infinite choice of names and you resort to your own, which you didn’t even choose for yourself. So you are both arrogant and stupid. Obviously, I’m being a little bit facetious, but I’m also not.
I’d read a book by Willard Manus called Mott the Hoople, which is quite a funny book. The titular character’s friend was called Frankie Pappas. And I thought, Jeez, that’s my mother’s maiden name, and I’d never seen Pappas in a book. So I was like, oh, this is funny. And Frankie is gender-neutral. And I thought, that’s interesting, maybe there’s something there. Anyone can be Frankie. But I always laugh when there’s a man that comes through asking for Mr Pappas, and then I’m like, well, that person definitely hasn’t read what we’re about.
And the reason we were in search for this collective pseudonym is that there was a mathematician called Nicolas Bourbaki who was releasing all these amazing papers on math, but it turned out like he was ten twenty-year-olds who had decided to collaborate under this collective pseudonym and they just changed mathematics. I think he is still, to this day, the most published mathematician. He’s multi-generational and we liked the idea of a multi-generational architectural firm in South Africa, because there aren’t that many of them. That’s why Frankie is Frankie.
Nicola Barrett: You state on your website that almost the entire tradition of Western formal architecture has produced sculpture rather than architecture. How so?
I think for a long time it has been the case. Formal architecture has always been something that you have to sell to someone. So whoever is the client, you have to give them drawings and models. It’s very difficult to make a drawing and make someone focus on the stuff that is inside the drawing. Like how the space solves these issues. Or you discuss the sculpture of the model and someone says, I don’t know how that looks. How do you discuss the space inside a model? It’s impossible. Informal architecture has been one of, what do I need? I need to solve this issue. I have another child. Therefore, there needs to be another bedroom. It’s a very practical thing.
I was in a competition and one of the guys was discussing the school he had made. This thing was clad in rock from the area and then one of these rock tiles had been removed, and then they put a stainless steel tile there. And he said, because we wanted the stainless steel to reflect the sky, and so, therefore, the sky would be bursting out from between the rocks. Why clad it in rocks in the fucking first place? There’s this obsession with what the thing looks like.
The most amazing photographs of the Pink Spot are the ones taken by Tshepiso Seleke. He does not give a shit about the architecture. He doesn’t care. He’s just like, there’s a beautiful person. There’s another beautiful person doing something. Doesn’t even look at the building. That shot that he took of those kids with those go-karts is just my favourite thing ever. That’s what I mean. There’s this obsession with what this thing looks like. That’s not the important stuff.
Nicola Barrett: What advice would you give to young creatives working in our architecture and design?
My only advice is that in the contemporary world, I think we are solving a lot of problems that are not actually problems. It’s like this artificial intelligence. This is a problem that is being solved that isn’t a necessary problem to solve. What is the actual improvement?
I suppose the thing is to see what are real problems and identify those as real problems and then solve those real problems. To actually be honest with oneself what real problems are. That’s not easy. We all get caught up in our own world. Taking a step back and thinking, where should I spend my time… Because you’ve got finite breath, right?
Many of us are incredibly doubtful in ourselves, stressed and worried. We think we are not big enough to contribute or to change everything, and we see these problems. But I think there are these small little things that we can get right and we can just try. The Pink Spot, just for the photos of those kids enjoying themselves, that makes it worth it. I always tear up when I see them. It’s so beautiful.